It is better to understand basic details to create a good alignment then copying someone else form.
What is Posture
A position of the body which is required to achieve a functional task by taking less muscle effort and creating maximum stability.
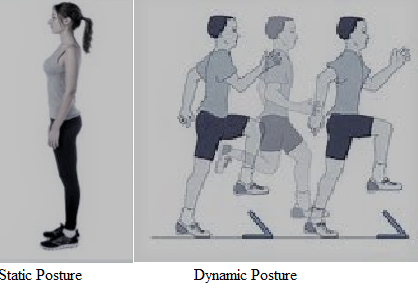
1. Static posture: Without doing any movement, how your body handles your body alignment, like sitting, sleeping and standing.
2. Dynamic posture: With functional activity, how your body manages to achieve the correct functional positions, like running, jumping and throwing or bending.
Postural Alignment
Proper body alignment depends on the curvature of the spine. The spine has three natural curvature at the neck, mid-back and lower back.
When any of these curvature increase or decrease or bent in sideways will create a postural misalignment lead to postural defects.
Factors which affect Posture
The chief factors affecting Body alignment:
1. Psychological background:-
A stable and positive mental attitude has a profound effect upon the nervous system and these effect reflected in the alignment of the body part of an individual.
2. Healthy Body:-
In terms with good health conditions, proper nutrition and appropriate sleep play an essential role for a healthy nervous system, and for the growth and development of bones and muscles.
3. Opportunity for plenty of natural free movement:-
Activities like jumping, running and outdoor activities enhance the opportunity of natural free movement resulting in the healthy development of skeletal muscle growth, which in turn helps to maintain good body alignment.
4. Local factors:-
localised pain, muscular weakness, occupational stresses etc. lead to muscular imbalance lead to altered postural pattern and even the cause of the pain has been removed, this adaptive altered pattern is continued and form a postural defect.
Pain and Posture Relation
People ask me many times, why some individuals with weak and stretched muscles may have no pain, but why the individual with tight and strong muscle shows pain.
I always say that the answer lies in mobility of that individual, as the one with weak muscle have flexible joints and position of the body also change randomly while on the other hand, the one with strong muscle have tightness in the muscle leads to less mobility which can cause painful incidents.
Basic understanding to relate with pain is the effect of constant or repeated smaller stress occurring over a prolonged period which can give rise to the same kind of pain that occurs with a sudden stress/injury.
From a physiotherapist's point of view, there is an important difference exist in between treatment of an acutely painful condition with that of a chronic one. Therapeutic treatment is only beneficial and relieves the pain if applied at the right time. Otherwise, the application of one may not give that much effect.
Posture Assessment
As a physiotherapist, I always look for the following basic principle to detect a faulty body alignment which are:
1. Faulty alignment - which results in undue stress and strain on bone, ligament, joints, and muscles.
2. Joint positions- Indicate which muscle is short and which is elongated.
3. A relationship findings between muscle and alignment of body segment to know if this alignment is habitual.
4. Muscle shortness - which holds the origin and insertion of the muscle close together.
5. Muscle weakness- allowing separation of muscle origin and insertion.
6. Adaptive shortening of the muscle - occur when muscle remains contracted for prolong period.
7. Stretch weakness - which occurs in one joint muscle that remains in an elongated position.
Examining the spine curvature is an important and most reliable way of knowing the postural defect is structural or adaptive.
What does an ideal Posture look like
No posture is said ideal.
Ideal body alignment is only a myth.
Body alignment is considered ideal only when the body can change its shape and alignment based on the functional movement it needs to achieve and the given task can be completed with a maximum output of stability while putting less effort of using muscle work.
With such efficiency, less number of repeated stress occurs and mobility increases.
Always try to change your position in every 15-20 minutes to avoid stresses on the body joint which can lead to adaptive postural changes.
Conclusion
Perfect Postural alignment is a myth any alignment providing maximum output with less muscular effort is considered good body alignment.
Avoid any kind of pressure and load on physical and mental health as both will affect the body alignment.
Avoid any type of sedentary lifestyle where sitting is needed for 8 hours straight, use an alarm clock, set a 20 min timer. when it rings stand up walk a little then come back to work.
Always remember never underestimate the power of good body alignment as it relieves 70% of your muscular pain.
Resources
- Muscles: Testing and function with posture and pain, 5th Edition - Kendall
- The Principle of exercise therapy, Fourth edition - M. Dena Gardiner.







0 Comments
Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box